


Critical to quality – attributes most important to the customer.GE outlines the key concepts that inform Six Sigma as follows: These calculations are rooted in mathematics and statistics and are further explained here and here. And, in electronics manufacturing, this measurement can be used in relation to anything from a component to a period of time.
Six sigma processes free#
A Six Sigma process is one in which 99.99966 per cent of products created are free of defects to put it another way, there should be no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO).Ī defect is anything that falls outside of a standard process – that is, a variation. The term "sigma" derives from the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet (Σ, σ, ς). It's essentially a quest for perfection – although, of course true perfection is impossible to achieve. Six Sigma revolves around reducing errors, to deliver better products and services – thereby improving the customer experience and increasing profit. "In contrast with other quality initiatives, Six Sigma recognises that there is a direct correlation between the number of product defects, wasted operating costs, and the level of customer satisfaction." So, what does it involve and what does it look like in practice? What is Six Sigma? Today, Six Sigma is utilised across industries. It is now an entrenched business philosophy at the organisation. Jack Welch, the former chairman and CEO of GE, made Six Sigma a core component of his business strategy during his twenty-year tenure. But it's not a mystery to be unravelled rather, it is a defined, data-driven methodology aimed at process improvement and consistent output in manufacturing.Īlthough it was originally developed by Motorola in 1986, Six Sigma is more commonly associated with General Electric (GE). Six Sigma: it sounds like something out of a Dan Brown novel.
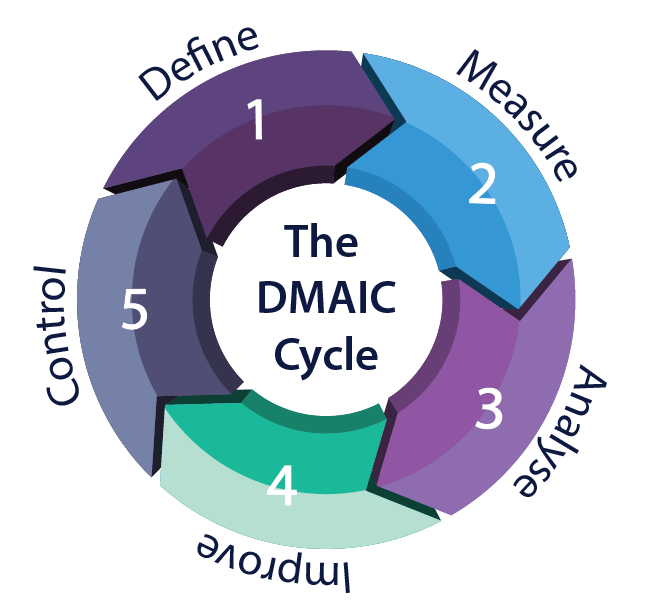
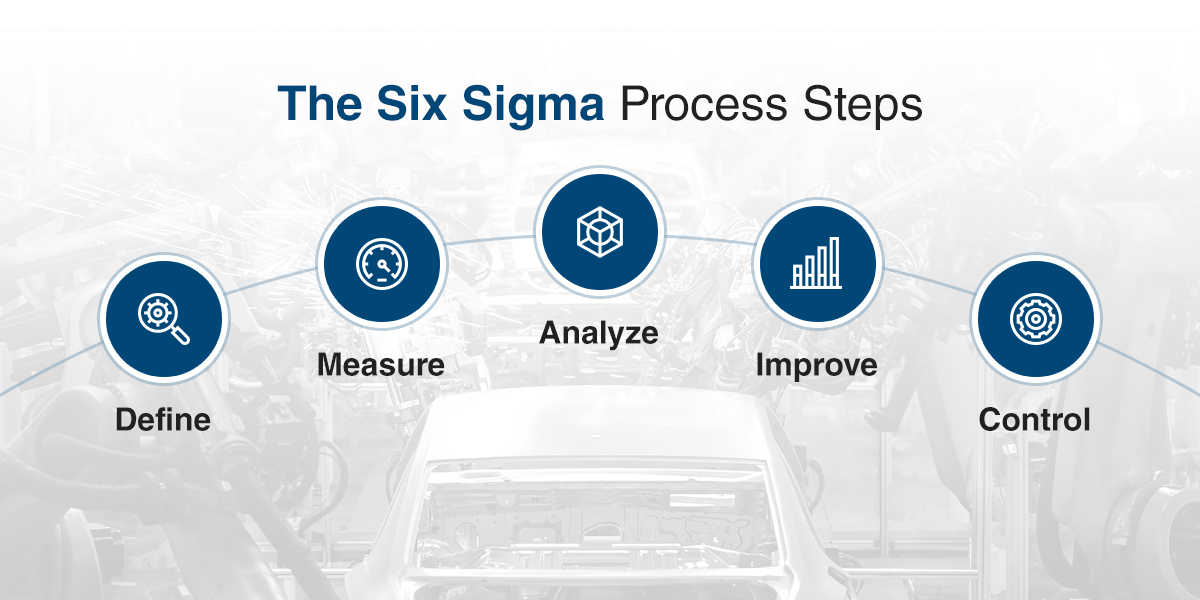
"Six Sigma is a quality programme that, when all is said and done, improves your customer's experience, lowers your costs, and builds better leaders."


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
